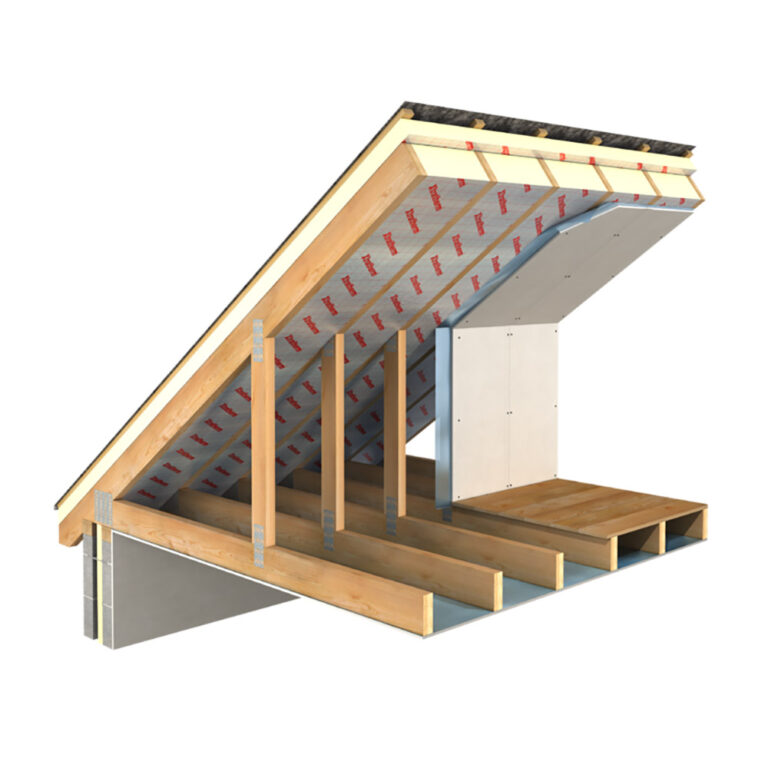
Best Insulation For Warehouse Ceiling
Best insulation for warehouse ceilings is a critical decision impacting energy costs, environmental responsibility, and worker comfort. This comprehensive guide explores various insulation types—fiberglass, cellulose, spray foam, and rigid foam—comparing their thermal performance, installation methods, fire safety, and long-term cost-effectiveness. We’ll delve into factors influencing insulationchoicese, such as climate, warehouse size, and contents, offering a decision-making framework to guide your selection. Furthermore, we’ll examine environmental considerationsand, regulatory compliance, and showcase successful insulation projects to illustrate best practices.
Understanding the nuances of warehouse insulation is key to optimizing energy efficiency and minimizing operational expenses. From initial cost analysis to long-term ROI calculations, this guide equips you with the knowledge to make an informed decision that aligns with your specific warehouse needs and budgetary constraints. We’ll examine best practices for installation and maintenance, ensuring your chosen insulation provides maximum benefit for years to come.
Types of Warehouse Ceiling Insulation
Choosing the right insulation for your warehouse ceiling is crucial for maintaining a comfortable working environment, reducing energy costs, and protecting your inventory. Several types of insulation offer varying levels of thermal performance, cost-effectiveness, and installation complexity. This section compares and contrasts four common options: fiberglass, cellulose, spray foam, and rigid foam.
Comparison of Insulation Materials
| Material | R-value (per inch) | Cost (Approximate) | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiberglass Batt | R-3 to R-6 | Low to Moderate | Easy to install, readily available, and relatively inexpensive. | Can settle over time, may not provide air sealing, potentially irritating to skin and lungs during installation. |
| Cellulose | R-3.1 to R-3.8 | Moderate | Good thermal performance, recycled content, and excellent air sealing properties. | Requires specialized equipment for installation, can be messy. |
| Spray Foam (Open-cell) | R-3.5 to R-4 | Moderate to High | Excellent air sealing, high R-value, and good moisture resistance. | Requiring specialized equipment and trained installers can be more expensive. |
| Spray Foam (Closed-cell) | R-6 to R-7 | High | Superior insulation value, excellent air, and moisture barrier, and high structural integrity. | More expensive, and requires specialized equipment and skilled installers. |
| Rigid Foam (Polyisocyanurate or Polyurethane) | R-6 to R-8 | Moderate to High | High R-value, durable, easy to handle and install. | Can be brittle, and requires careful handling to avoid damage. |
Insulation Installation Methods, Best insulation for warehouse ceiling
The installation method varies significantly depending on the chosen insulation type and the existing ceiling structure. Proper installation is crucial for achieving optimal thermal performance and preventing future problems.
- Fiberglass Batt: Installed between joists or rafters, requiring careful fitting to minimize gaps. Existing ceiling structures might require the removal of sections for proper installation.
- Cellulose: Typically blown into place using specialized equipment. Existing ceiling structures might require drilling small holes for injection.
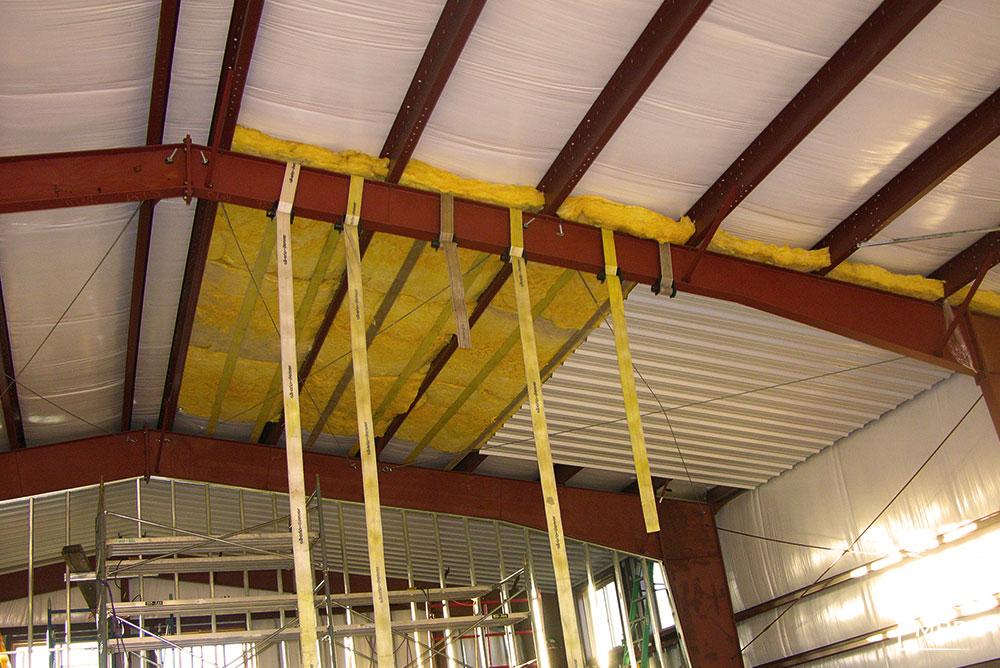
- Spray Foam: Applied directly to the ceiling surface using specialized spray equipment. Existing structures require thorough cleaning and preparation.
- Rigid Foam: Installed as panels or boards, adhered or mechanically fastened to the ceiling. Existing structures may need surface preparation for proper adhesion.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Each insulation type possesses different fire resistance properties. Understanding these properties is crucial for ensuring warehouse safety and compliance with fire codes.
- Fiberglass: Generally considered non-combustible, but can act as a fuel source if exposed to intense heat for prolonged periods.
- Cellulose: Treated with fire retardants to enhance fire resistance. However, proper installation is crucial to prevent the formation of air pockets.
- Spray Foam: Open-cell spray foam is less fire-resistant than closed-cell, which has a higher fire rating and acts as a fire barrier.
- Rigid Foam: Offers good fire resistance, with variations depending on the specific type of foam used. Often includes fire retardant additives.
Factors Affecting Insulation Choice

Source: insulatewithallied.com
Several factors influence the optimal insulation choice for a warehouse ceiling. Careful consideration of these factors ensures a cost-effective and efficient solution tailored to the specific needs of the facility.
Climate Conditions and Warehouse Characteristics

Source: metalbuildingpriceguide.com
Climate significantly impacts insulation needs. Extreme temperatures and high humidity necessitate higher R-values to maintain consistent internal temperatures and prevent moisture damage.
- Temperature Extremes: Colder climates require higher R-values to minimize heat loss, while hotter climates need insulation to reduce heat gain.
- Humidity: High humidity can lead to condensation and mold growth within the ceiling cavity, necessitating insulation with good moisture resistance.
- Warehouse Size and Height: Larger warehouses with high ceilings require more insulation to maintain consistent temperature control, potentially influencing the choice of insulation type due to installation complexity.
- Warehouse Contents: Storing frozen goods necessitates insulation with exceptional thermal performance to minimize energy consumption, whereas flammable materials necessitate insulation with high fire resistance ratings.
Decision Tree for Insulation Selection
A decision tree can guide the selection process. This example simplifies the decision-making process based on key factors.
(A visual decision tree would be included here, but cannot be rendered in plain text. It would start with a question about climate (extreme/moderate), branch to questions about warehouse size/height (large/small), and finally to content type (frozen/flammable/general) leading to recommendations for insulation types.)
Cost and ROI of Warehouse Ceiling Insulation
While the initial investment in warehouse ceiling insulation can be significant, the long-term cost savings often justify the expense. This section analyzes the cost breakdown and return on investment (ROI) for different insulation options.
Initial Costs
Initial costs include material, labor, and installation. Prices vary depending on the size of the warehouse, insulation type, and labor rates in the region.
(A table comparing initial costs for different insulation types per square foot would be included here, but cannot be created in plain text. It would include columns for material cost, labor cost, and total cost for each insulation type.)
Long-Term Cost Savings
Improved energy efficiency through better insulation leads to reduced energy bills. This translates into significant cost savings over the lifespan of the warehouse.
(A table comparing long-term cost savings over 10 years for different insulation types will be included here. It would show projected energy costs with and without insulation for each option, highlighting the net savings.)
For example, a warehouse with poor insulation might spend $10,000 annually on heating and cooling. With proper insulation, this could be reduced to $6,000, resulting in a $4,000 annual saving and a significant ROI over 10 years.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and regular maintenance are vital for maximizing the lifespan and performance of warehouse ceiling insulation. This section Artikels best practices and potential issues.
Best Practices for Installation

Source: ytimg.com
- Ensure proper vapor barrier installation to prevent moisture damage.
- Minimize gaps and air leaks during installation to maximize thermal performance.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for each insulation type.
- Use appropriate safety equipment during installation.
Potential Installation Problems and Prevention
- Sagging: Use proper support structures for batt insulation to prevent sagging.
- Air Leaks: Seal all gaps and cracks thoroughly to prevent air infiltration.
- Moisture Accumulation: Ensure proper vapor barrier installation to prevent moisture buildup.
Maintenance Requirements
- Regular Inspections: Inspect for signs of damage or deterioration.
- Cleaning: Remove any dust or debris buildup.
- Repair: Repair any damaged sections promptly.
- Replacement: Replace insulation when necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Environmental Considerations: Best Insulation For Warehouse Ceiling
Choosing environmentally friendly insulation contributes to a smaller carbon footprint and a more sustainable warehouse operation. This section examines the environmental impact of different insulation options.
Environmental Impact of Insulation Materials
The environmental impact of insulation materials varies based on their manufacturing process, energy consumption during production, and recyclability. For example, cellulose insulation often utilizes recycled materials, making it a more sustainable choice than some foam insulations which may have higher embodied carbon.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
Effective insulation reduces energy consumption for heating and cooling, directly decreasing a warehouse’s carbon footprint. This contributes to broader sustainability goals and can improve a company’s environmental image.
Sustainable Insulation Options
Several sustainable insulation options are available, including cellulose, recycled denim insulation, and certain types of plant-based foam insulation. These options often have lower embodied energy and are more readily recyclable than traditional options.
Regulatory Compliance and Building Codes
Warehouse ceiling insulation must comply with relevant building codes and regulations. This section Articulates key considerations for ensuring compliance.
Relevant Building Codes and Regulations
Building codes vary by location but generally address fire safety, energy efficiency, and insulation requirements. It is crucial to consult local building authorities to ensure compliance.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance

Source: com.au
Compliance involves careful selection of insulation materials, proper installation methods, and adherence to all specified standards. Engaging qualified professionals for design and installation helps to ensure compliance.
Incorporating Energy Efficiency Standards
Incorporating energy-efficient insulation into warehouse design and construction minimizes long-term energy costs and reduces the environmental impact of the building. This aligns with broader sustainability initiatives and often results in cost savings.
Case Studies of Warehouse Insulation Projects
Real-world examples illustrate the benefits of warehouse ceiling insulation and highlight successful project implementations. These case studies provide valuable insights into different approaches and outcomes.
Case Study 1: Cold Storage Facility
This cold storage facility in a northern climate experienced significant energy savings after installing closed-cell spray foam insulation. The improved insulation reduced energy consumption by 30%, resulting in substantial cost savings and a faster ROI than initially projected. The choice of closed-cell spray foam was driven by the need for superior thermal performance and moisture resistance in a cold, humid environment.
Case Study 2: Distribution Center
A large distribution center in a hot, arid climate opted for rigid foam insulation due to its ease of installation and high R-value. The project successfully improved temperature control within the warehouse, reducing energy costs and creating a more comfortable work environment. The challenges included proper sealing of the panels to prevent air infiltration.
Case Study 3: Manufacturing Warehouse
This manufacturing warehouse, storing both flammable and non-flammable materials, prioritized fire safety and energy efficiency. They chose a combination of fire-rated mineral wool insulation and sealed rigid foam panels. The project successfully met both fire safety codes and improved energy efficiency. The design addressed the unique requirements of storing various materials with different flammability ratings.
Essential FAQs
What is the lifespan of different warehouse ceiling insulation types?
Lifespans vary. Fiberglass and cellulose generally last 15-30 years, while spray foam and rigid foam can last 50 years or more with proper installation and maintenance.
Can I install warehouse ceiling insulation myself?
While DIY is possible for some types (like fiberglass batts), professional installation is often recommended, especially for spray foam and complex ceiling structures, to ensure optimal performance and avoid potential issues.
How often should I inspect my warehouse ceiling insulation?
Regular inspections (at least annually) are recommended to check for damage, settling, or moisture accumulation. More frequent inspections may be necessary depending on the insulation type and warehouse environment.
Are there tax incentives or rebates available for warehouse insulation upgrades?
Yes, many regions offer tax credits or rebates for energy-efficient upgrades, including warehouse insulation. Check with your local and national government agencies for available programs.
What are the potential health risks associated with different insulation materials?
Some insulation materials may contain irritants or allergens. Always follow manufacturer safety guidelines during installation and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).