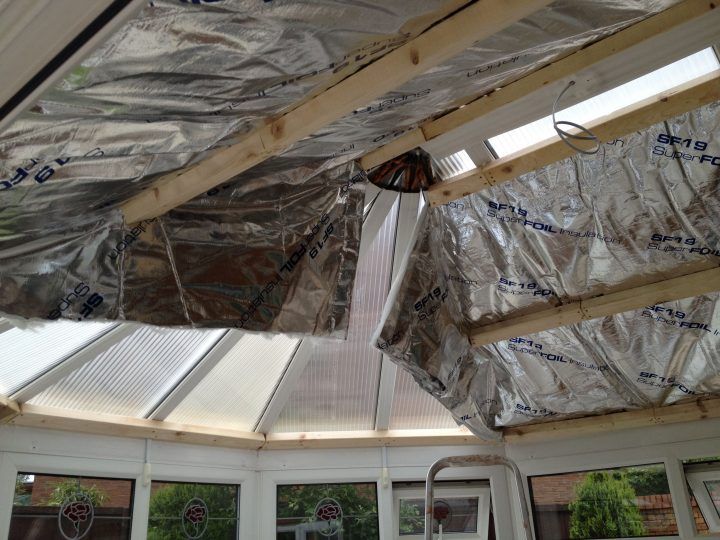
Insulation For Metal Building Roof
Insulation for metal building roofs is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient interior environment. Metal roofs, while durable and aesthetically pleasing, are notorious for their thermal conductivity, leading to significant heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter. Choosing the right insulation type, however, can dramatically improve the building’s energy performance and longevity, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. This exploration delves into the various aspects of selecting and installing effective roof insulation for metal buildings, covering material types, installation techniques, cost-benefit analyses, and environmental considerations.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of insulation options for metal building roofs, ranging from spray foam and fiberglass batts to rigid foam boards and mineral wool. We’ll examine the thermal performance, installation methods, and long-term implications of each choice, helping you make an informed decision based on your specific needs and budget. Understanding the nuances of vapor barriers and addressing potential installation challenges are also key components of this discussion, ensuring your building remains protected and energy-efficient for years to come.
Insulation Types for Metal Building Roofs
Choosing the right insulation for your metal building roof is crucial for energy efficiency, comfort, and longevity. Several factors influence this decision, including climate, budget, and building code requirements. This section details the characteristics of common insulation materials, allowing for informed selection based on specific needs.
Comparison of Common Insulation Materials
Several insulation types are suitable for metal building roofs, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. The following table compares spray foam, fiberglass batts, rigid foam boards, and mineral wool based on their thermal performance, cost, and other key factors.
| Insulation Type | R-Value (per inch) | Cost | Installation Difficulty | Lifespan | Environmental Impact | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spray Foam | 6.0 – 7.0 | High | Medium-High | High | Medium | Suitable for various climates and roof designs; excellent air sealing properties. |
| Fiberglass Batts | 3.0 – 4.0 | Low | Low | Medium | Low to Medium | Best suited for milder climates and simpler roof designs; requires careful installation to avoid gaps. |
| Rigid Foam Boards (Polyisocyanurate or Polyurethane) | 6.0 – 8.0 | Medium | Medium | High | Medium | Versatile option for various climates and roof designs; good for flat or low-sloped roofs. |
| Mineral Wool | 3.0 – 4.0 | Medium-High | Medium | High | Low | Good for fire resistance and sound dampening; suitable for various climates but can be more expensive. |
Note: R-values can vary depending on the specific product and thickness. Cost estimates are relative and can fluctuate based on market conditions and location.
Installation Methods and Best Practices
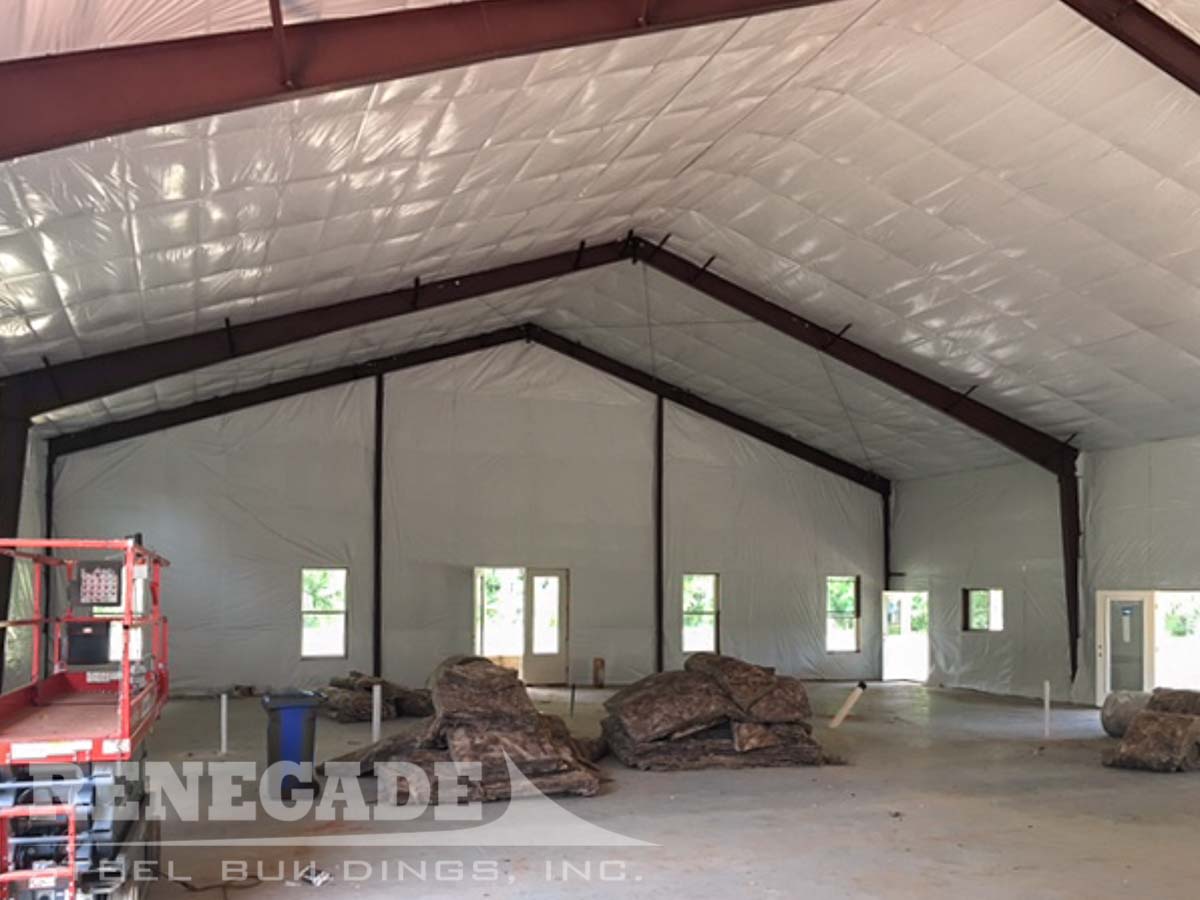

Source: renegadesteelbuildings.com
Proper installation is critical for maximizing the effectiveness of any insulation. The following Article the process for two common types: fiberglass batts and rigid foam boards.
Fiberglass Batt Installation
1. Prepare the roof deck: Ensure the surface is clean and free of debris. 2. Measure and cut batts: Accurately measure the spaces between rafters or purlins. 3. Install batts: Carefully fit the batts snugly between the structural members, avoiding compression. 4. Secure batts: Use appropriate fasteners to hold the batts in place, preventing shifting. 5. Install vapor barrier: Place a continuous vapor barrier over the insulation to prevent moisture intrusion.
Rigid Foam Board Installation
1. Prepare the roof deck: Clean and ensure a level surface. 2. Measure and cut boards: Precisely measure and cut the boards to fit the roof sections. 3. Install boards: Begin at the lowest point of the roof and work upwards, ensuring tight seams between boards. 4. Secure boards: Use appropriate adhesive and mechanical fasteners to secure the boards firmly to the roof deck. 5. Install vapor barrier: Apply a continuous vapor barrier over the foam boards.
Insulation Installation Checklist
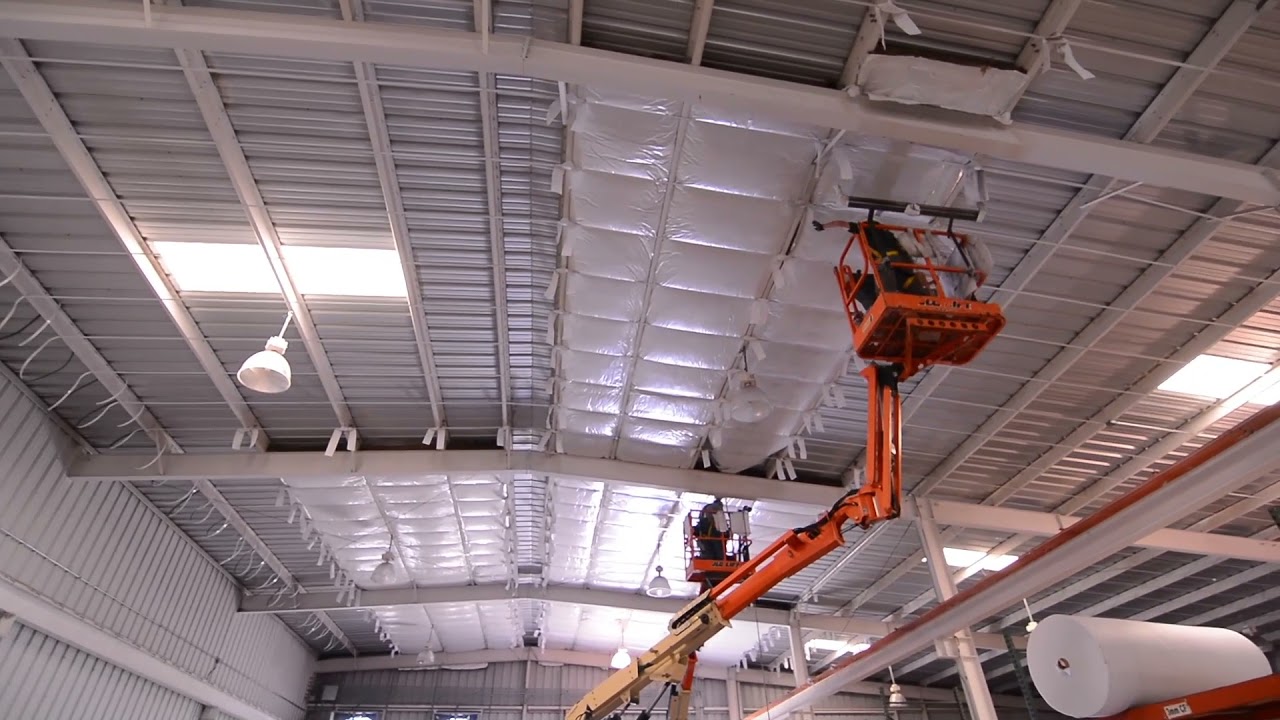

Source: ytimg.com
- Clean the roof deck before installation
- Accurate measurements and cutting of insulation
- Proper fitting of insulation to avoid gaps and air leakage
- Secure fastening of insulation to prevent shifting
- Continuous and properly sealed vapor barrier
- Inspection for thermal bridging and air leakage after installation
Vapor Barrier Importance and Material Selection, Insulation for Metal Building Roof
A vapor barrier is essential to prevent moisture from entering the insulation, which can lead to mold growth and reduced effectiveness. Suitable materials include polyethylene sheeting, foil-faced insulation, and specialized vapor retarders. Proper placement is crucial; generally, it’s installed on the warm side of the insulation.
Factors Affecting Insulation Choice: Insulation For Metal Building Roof
Several factors play a significant role in determining the most suitable insulation for a particular metal building roof. These factors must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Key Factors Influencing Insulation Selection
- Budget: Insulation costs vary significantly; balancing cost with performance is crucial.
- Climate: Colder climates require higher R-values than warmer climates.
- Building Code Requirements: Local codes may specify minimum insulation levels.
- Roof Design: Complex roof designs may necessitate specialized insulation techniques.
Insulation Performance in Different Climates
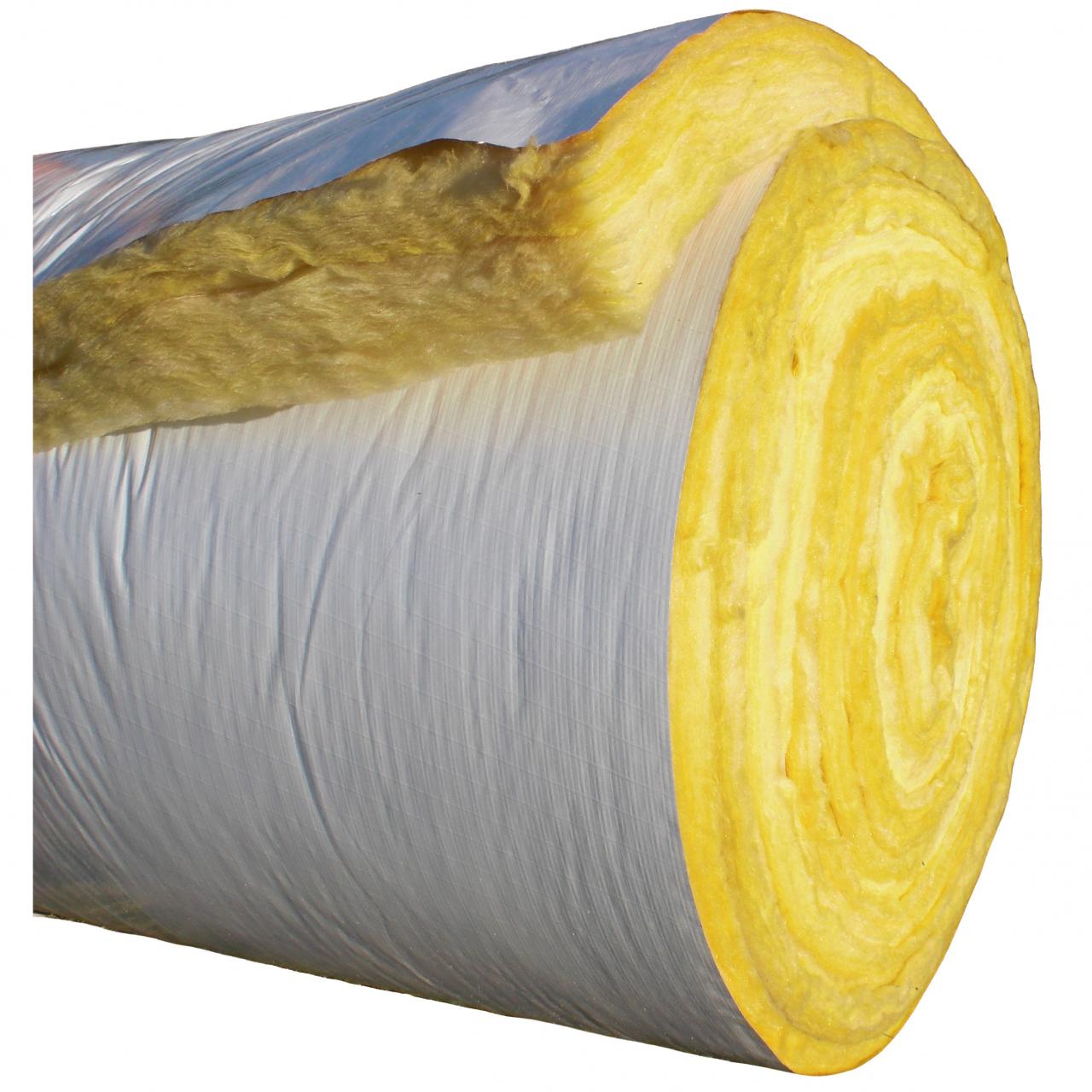

Source: awmetal.net
In hot and humid climates, insulation with high thermal resistance and good moisture resistance is crucial to prevent condensation. In cold and snowy climates, insulation with high R-values is necessary to minimize heat loss and prevent ice dam formation. Spray foam and rigid foam boards are often preferred in extreme climates due to their superior thermal performance and air-sealing capabilities.
Addressing Unique Insulation Challenges in Metal Building Roofs
Metal roofs can present challenges due to their thermal conductivity. Proper insulation placement and attention to detail such as thermal bridging are critical to prevent heat transfer. Using continuous insulation systems can help mitigate these issues.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Proper roof insulation significantly impacts energy efficiency and reduces heating and cooling costs. The following explores the potential cost savings and available incentives.
Potential Energy Savings through Roof Insulation
The amount of energy saved depends on factors like the existing insulation level, climate, and building size. For example, upgrading from R-13 to R-30 insulation in a typical metal building could reduce heating and cooling costs by 20-30%, depending on the climate and building design. This translates to significant savings over the lifespan of the building.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Insulation Investment
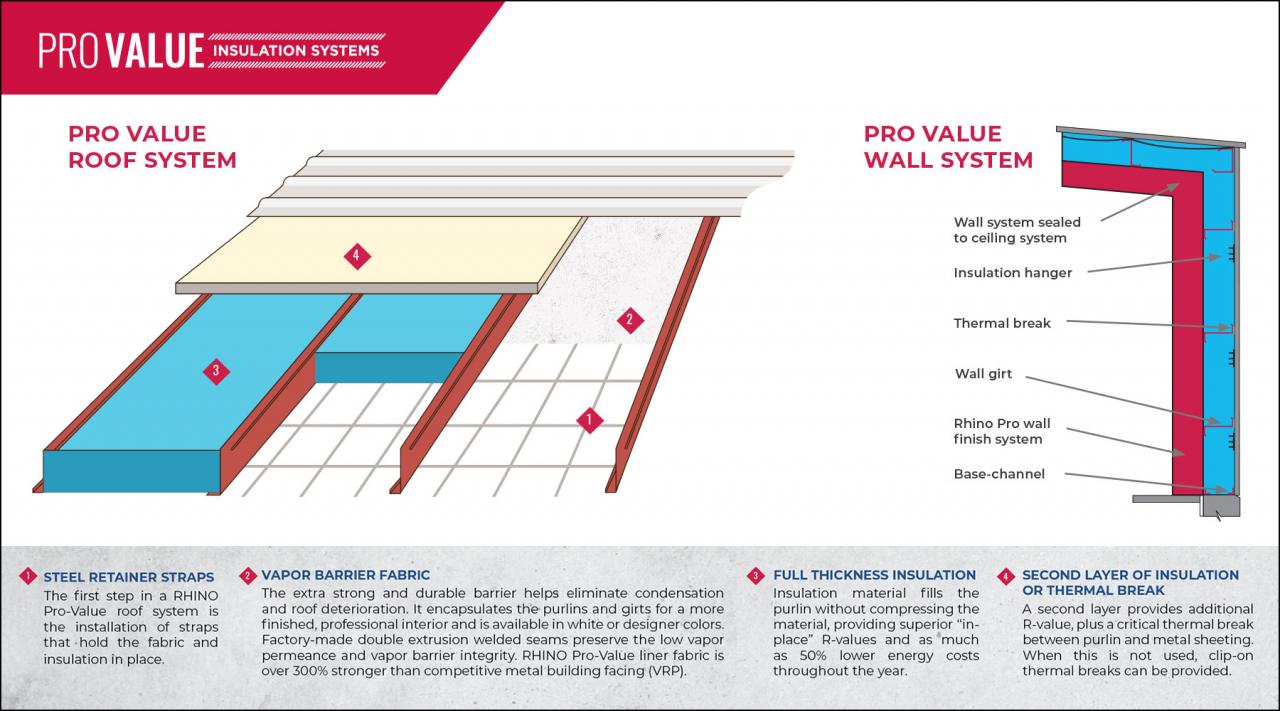
Source: rhinobldg.com
While the initial investment in insulation can be substantial, the long-term energy savings typically outweigh the initial cost. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, considering factors such as energy prices, insulation lifespan, and potential rebates, should be performed before making a decision.
Government Incentives and Rebates
Many governments offer financial incentives and rebates for energy-efficient building practices, including roof insulation. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of insulation and accelerate the return on investment.
Maintenance and Lifespan of Insulation
Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the long-term effectiveness of roof insulation. This section Artikels common issues and maintenance guidelines.
Common Insulation Problems and Maintenance
- Moisture Intrusion: Proper vapor barrier installation and regular inspections are vital to prevent moisture damage.
- Settling of Insulation: Loose-fill insulation may settle over time, reducing its effectiveness. Periodic checks and top-ups may be needed.
- Pest Infestation: Some insulation types may attract pests. Regular inspections and appropriate pest control measures can prevent this.
Addressing Common Insulation Problems
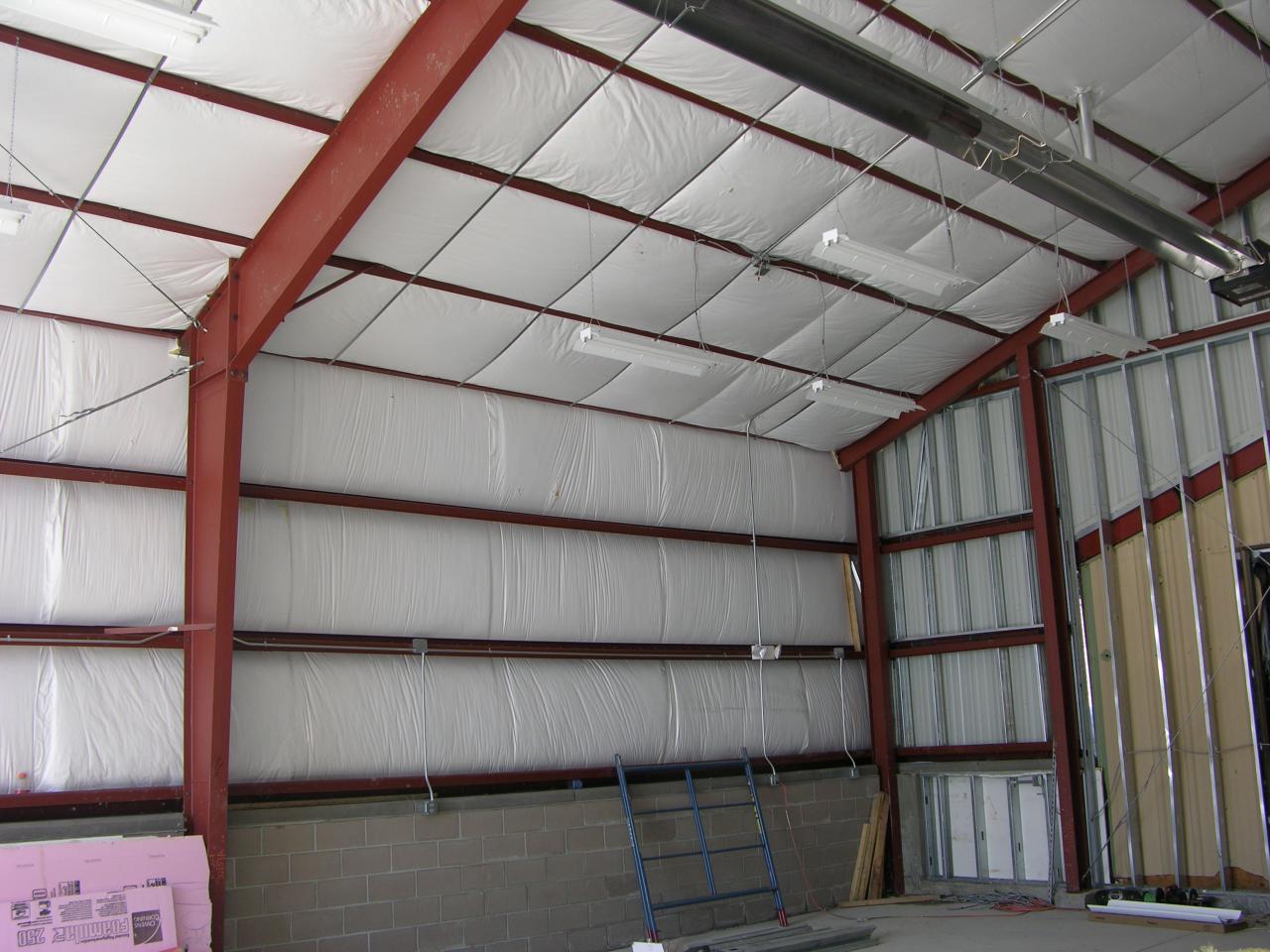

Source: pinimg.com
Moisture intrusion can be addressed by repairing damaged vapor barriers and ensuring proper ventilation. Settling of loose-fill insulation can be remedied by adding more insulation. Pest infestations require professional pest control services.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of insulation materials should be considered when making a selection. This section compares the environmental footprint of different options.
Environmental Impact of Insulation Materials
The environmental impact of insulation materials varies. Fiberglass insulation, for example, has a relatively low embodied carbon compared to spray foam. Mineral wool is often considered a sustainable option due to its recycled content and recyclability. However, the manufacturing process of each material has its environmental considerations, which should be weighed carefully.
Embodied Carbon Comparison of Insulation Options
Embodied carbon refers to the greenhouse gas emissions associated with the manufacturing, transportation, and installation of a material. A comparative analysis of the embodied carbon of different insulation options is crucial for environmentally conscious building projects. This data is typically available from manufacturers or independent sustainability assessments.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Insulation Choices
Choosing eco-friendly insulation contributes to a more sustainable building. Options include recycled-content insulation, rapidly renewable materials, and insulation with low embodied carbon. Consider the entire lifecycle of the insulation material, from manufacturing to disposal, when making your selection.
Top FAQs
What is the typical lifespan of different roof insulation materials?
Lifespans vary. Spray foam can last 50+ years, while fiberglass batts might need replacement after 15-20 years. Rigid foam boards generally last 30-50 years.
Can I install roof insulation myself, or should I hire a professional?
While some types are DIY-friendly (e.g., batts), professional installation is often recommended, especially for complex roofs or spray foam, to ensure proper air sealing and prevent future problems.
How do I determine the appropriate R-value for my climate?
Consult local building codes and energy efficiency guidelines for recommended R-values in your region. Higher R-values generally mean better insulation in colder climates.
Are there any government incentives or rebates available for roof insulation?
Yes, many governments offer tax credits, rebates, or other incentives for energy-efficient upgrades, including roof insulation. Check with your local or national energy agencies for available programs.
What should I do if I suspect moisture intrusion in my roof insulation?
Immediately contact a qualified roofing professional to inspect and address the issue. Moisture can severely damage insulation and lead to structural problems.





